Cryptocurrency Security: The Truth You Need To Know
When Satoshi Nakamoto launched Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, the developers and early investors were highly optimistic because they had found a way of countering distrust from centralized entities and intermediaries.
The design with highly sophisticated encryption, decentralized structure, and irreversible transactions was expected to make the system inviolable and unhackable.
However, things do not appear to follow these expectations. The system has become vulnerable to high tech criminals and even human error.
The security lapses that are emerging in the blockchain sector are subjecting the digital asset owners to serious risks;
- What are the different types of crypto-related security vulnerabilities?
- Must a person be a tech wizard to stay safe when operating in the blockchain niche?
- Which is the most common security threat in the blockchain niche?
- What is the best way to reduce these threats?
- What resources are required to lower crypto related security risks?
This guide was created to provide cryptocurrency owners and enthusiasts with comprehensive answers to the above questions.
Table of Contents
- Section One: Getting Your Cryptocurrencies Safe: This section describes the importance of reducing the threat of cryptocurrency security risks.
- Section Two: Important Cryptocurrency Concepts You Need To Know Today. This part demonstrates the basic ideas that support the later sections (how to) brought out in section three.
- Section Three: Taking On the Challenge of Cryptocurrency Security. This section is a detailed how-to info on detecting and avoiding key security vulnerabilities.
Getting Your Cryptocurrencies Safe
From the start, when the Bitcoin protocol was released in 2009, cryptocurrency ownership has given investors a very motivating experience.
The bulk of this motivation arises from factors like the potential for gains (or losses) in coin value or even the emerging possibility of regulation. Most of the factors affecting the value are way above investor control.
Another serious risk of the danger of security breaches. Though investors have significant control over the danger of losing coins in the event of a security breach, no guarantees are provided. To keep your coins safe, it is important to combine knowledge, vigilance, and discipline when operating in the niche.
The Rise in Cryptocurrency Values Reflect the Growing Need for Security

Willie Sutton, one of the famous American robbers, was once asked why he robbed banks. He is reported to have replied, “That is where the money is?”
In the same spirit, the rate and value of security breaches against cryptocurrency owners have been going up. Why the upward trend? Because user numbers and value of the cryptocurrencies are on an upward trend.
Take the case of 2017 statistics on cryptocurrencies captured by The Telegraph.
- As the price of Bitcoin shot from about $1,000 to near $20,000 mark in 2017, crimes associated with it rose by more than 200%.
- One in every ten owners of cryptocurrencies was at risk of getting affected by scams.
- Investors lost $225 million due to phishing scams.
- Ethereum-related cybercrime alone resulted in about 30,000 owners getting scammed.
- About $390 million was lost to cybercriminals.
To succeed in your cryptocurrency investment, you need to keep the coins safe.
This guide was created to help people holding crypto coins or prospective investors identify, detect, and recover (where possible) from various security vulnerabilities.
How Do Cryptocurrency Owners Lose Their Coins?
If you follow many people who promote cryptocurrencies, you will realize that they mainly focus on the positive side of owning the coins.
This guide is different.
We combined an inclusive list of key security problems that you should anticipate when investing in cryptocurrencies. We are not trying to pose the cryptocurrencies in lousy light. We will also focus on how those in cryptocurrencies can detect and even avoid related loss and crime.
The following scenarios depict the negative side of investing in cryptocurrencies that many promoters rarely tell you.
Investors often lose their coins through;
- Losing or forgetting their private keys (coded access codes).
- Lack of ample awareness and resources to keep cryptocurrencies safe.
Criminals are becoming very sophisticated and are using advanced technologies.
- They get access to coin owners’ private keys and demand a ransom to release the keys.
- They gain access and divert computer resources of the coin owners (without the knowledge or owners) and use them in different money making schemes.
- They trick owners into believing they are genuine service providers or blockchain project startups.
- They break into different digital storage spaces and siphon users coins into their accounts.
- They fool coin owners and make them behave in a way that crooks gather information about them.
- They trick people to invest in startups that are designed as Ponzi schemes.
- They infect good websites with malware targeting to access and steal users’ private keys and seed phrases.
The above security risks and misfortunes demonstrate the diverse themes of deception, theft, and use of malware.”
Important Cryptocurrency Concepts You Need To Know Today
Before diving deeper into the methods you can use to challenge the security risks, it is prudent to take a closer look at some of the basic ideas that the cryptocurrency security is premised on. We identify the basic idea, the relation to security, and give references to other sources for additional details.
The blockchain and cryptocurrencies
Here, we presume you are familiar with the two primary concepts. The blockchain is a digitized and decentralized public ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. The progressively growing blocks are recorded in the public ledger chronologically. Cryptocurrency, on the other hand, is a digital currency that utilizes cryptography for security to make it difficult to counterfeit for its advanced features. If you need, consider refreshing your memory of the two concepts here and here.
The cryptocurrency encryption and storage
In the crypto niche, protecting and storing digital coins are the core elements needed for success. The crypto networks provide users with complex codes for protection while wallets and digital exchange offer storage and facilitate transactions.
- A cryptocurrency wallet: This is a digital storage space designed to help people hold and manage their coins. You can opt to use a hot wallet (connected to the internet) or cold storage (offline and considered more secure).
- Private keys: This is a set of codes that combines numbers and letters to provide users with access to their wallets. The private key is also important in helping users run transactions such as sending coins from that wallet. It is prudent that the private key is kept private all the time because a person with the key can easily access your wallet.
- Public address: This is another code containing strings of characters and used to serve as the main address to your wallet. Unlike the private keys, the public address is fully open and can be given to your payers.
Encryption
Encryption involves hiding data by converting it to a special code that can be transmitted through cryptocurrency networks without easily getting revealed. To get the encrypted data, the targeted recipient is required to have a decryption code. These decryption codes are referred to as keys.
Asymmetric cryptography
When using two-key encryption, the security is provided on two important pieces of information referred to as the private-public key pair.
Public key gives the location where the coins are stored online. The private key helps to decrypt and reveal the information about the stored coins. The data that is stored on the blockchain includes the validation of the location, amount, and ownership.
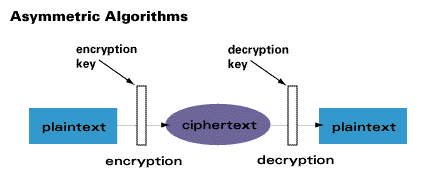
The private keys info has become the primary target of cybercriminals. They employ various tactics such as breaking through installed security walls to gain access to the private keys. They steal the keys because digital coins lack a physical form, the way we know dollars or Euros.
The main key to understanding cryptocurrency security is this; the person with the private keys validation info is the owner of the currency. Therefore, you lose the private keys; you lose the cryptocurrency.
Wallets
Irrespective of the cryptocurrency of interest, the private keys will need to be stored securely somewhere. That location where you store the coins is called a digital wallet.
The cryptocurrency wallet can be an online wallet or third-party service such as the exchanges. You can also opt to store the coins in offline storage such as hardware or paper wallets.
The level of risk security: The longer the wallet you are using to store the tokens is connected to the internet, the higher the danger of losing the coins.
- Hot wallets: These are online exchanges that can be accessed using applications or Web Browsers. They are referred to as “Hot” because they are always online. This implies that they are more vulnerable to malware attacks.
- Cold wallet: Unlike the hot wallet, the cold wallet stores the coins offline. This implies that the hackers do not have the internet connection to the wallet or private keys and cannot break in.
- Hardware wallet: These are small finger-sized hardware devices that look like standard USB drives. They are physical devices that can be used to store and run transactions. Every hardware wallet is sold with a private key that provides the user with respective validation info. If you cannot get the blockchain information, the coins will be inaccessible.
- Paper wallets: This involves writing the private key code on a paper and securing it offline.
If you want to store the tokens safely, you would need to use two digital wallets; hot wallet for running transactions, and cold wallet for storing the coins especially on the long-term.
NOTE: It is a security best practice to back up your private keys for all the wallets and securing them offline.
Cryptomining
When the first system for mining was set up in 2009, the potential was only for 21 million Bitcoins. But only about 17 million Bitcoins are in use.
Crypto mining is the process of releasing new coins into the system. The process involves gathering and verifying the blockchain transactions of the respective network and releasing new blocks into the public ledger.
The procedure involves miners who are required to solve complex mathematical puzzles to get the opportunity to verify the transactions. The first one to get the puzzle right gets the chance to add the new block and gets rewarded with native coins. To remain competitive (confirm more transactions) you will need specialized hardware such as GPU and ASICs that generate a lot of hashing power.
Key attack opportunities used by fraudsters at this point include:
- The hackers can steal the coins directly from cryptomining companies.
- Tricking the cryptominers to make them buy non-existent computer hardware.
- The cloud mining firms lending cryptocurrency miners at prices higher than they will earn. They offer profit by simply taking the coin value from all the new users which is a classic form of Ponzi scheme.
Cryptocrime Tactics
For people who closely follow the crypto news, the list of crimes is indeed long. They range from shady dealings to spoofs that target those with the coins. Here are some of the terms you need to know and that will help you remained informed. How many of these do you know?
- Social engineering: This is a general term used to denote a criminal fooling the target to get some advantage such as revealing the private keys. Since it is used as a means to an end, it is taken as a preface to other more serious criminal activities such as cryptojacking.
- Phishing: This involves the criminal presenting the target with the false pretext of a company, individual, organization or even government agency to prompt them taking action such as opening a malware. In the crypto niche, the phishing attacks end up into wallet break-ins or ransomware that involve stealing the user’s private keys.
- Cryptojacking: This is a strategy used by criminals to divert the cryptocurrency holder’s resources without their permission. The criminal tactic is used in crypto industry to divert mining resources of the target’s computer to mine cryptocurrencies.
- Breaking into online wallets and vaults of the exchanges: This method involves using false identities to get the user’s private information.
- Malvertising: This name tells the entire story. In this tactic, the criminals use malicious ads to spread malware to the targeted clients. The criminals target compromising web browsers and their plug-ins.
- ICO exit scams: This method has become very common resulting in the banning of many ICOs in some countries. It involves establishing an ICO, publicizing it, and persuading investors to buy the tokens. The scammers even reward the buyers who refer new clients. Then, they run away with the investors’ money. This is the standard form of an ICO scam.
- Poisoned website: This term is used to denote a site that criminals use to deliver malware. The malware is mainly carried as an ad.
- Phone porting: This attack method is a combination of hacking, phishing, and outright breaking into a target wallet. The hackers snoop in various places such as crypto-related conversion platforms, social media, and other platforms where investors post their details such as email and phone numbers. Once the scammers have all information about you, they pose as victims, call the phone provider, and persuade the customer support to transfer the number to a device they control.
Once the hackers have taken control over your number, they access your cryptocurrency exchange account, compromise the password, use the phone number for the second-factor authentication, and siphon away the coins.
- Spear phishing: This attack method involves targeting a specific organization or individual of interest. The attack can take place prior to stealing user data or installing malware into the target computer.
How Do You Secure Coins When Trading and At Home
In many forums, you will hear many analysts indicating that the only safe method of storing coins is through cold storage. However, this is a great option especially for those who target long-term storage. However, you will at some point need to transfer the coins to another wallet or exchange them.
The following are great tips you can use to keep the coins safe:
Isolate the Investment
Isolating the investment involves using a dedicated computer for transactions to and from the wallet. The process involves creating an air gap around the computer by ensuring that it is not connected to the internet when no transactions are running.
You can also isolate the computer by ensuring it can only connect to the network through another computer (gateway).
The method is one of the simplest to use. Connect the computer when running a transaction and disconnect immediately after the transaction is completed.
Remember that the computer should not be used for any other task.
Securing Yourself When Trading Cryptocurrencies
Isolating the computer is the first line of defense for protecting your tokens. You should also use the following tactics to keep them secure when exchanging the coins.
-
- Secure your computer’s operating system: Consider installing the operating system on a new computer or format the hard drive before reinstalling the preferred OS.
- Identify and use a reliable password manager: Many people have lost their coins because of forgetting one or several codes in their private keys. To avoid making this mistake, consider using a good password manager. This means that you can rest easy without worrying of ever forgetting or keying the wrong codes.
- Employ 2-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication helps coin owners to use two steps such as password and phone number for enhanced security. You can opt to include an SMS or email for confirmation before getting access to a wallet. This means that even if the attacker manages to break through the first layer, it will still be impossible to siphon the tokens without your email or phone.
- Consider using a hardware wallet: Hardware wallets are considered the safest when storing coins because they are always offline. Some are even designed to facilitate transactions without the keys leaving the hardware.
- Utilize virtual private network (VPN): VPNs are considered very secure when transferring important information across the internet by encrypting the path. In the cryptocurrency systems, VPNs encrypts the network path followed by the coin from the sender to the destination. It is very important to use VPN, especially when using a network that you do not control.
Taking On the Challenge of Cryptocurrency Security
Today, Bitcoin stands out for being the oldest cryptocurrency in the blockchain niche. It is also the most successful in terms of price and adoption across the globe. Despite this success, many security issues about BTC have emerged because of its vulnerability to the rising number of illegal traders or attacks on the exchanges and storage pools.
Bitcoin protocol was created on the proof of work (PoW) consensus algorithm, which allows transactions to be run in a decentralized, secure, and peer2peer basis. Because the platform does not require a centralized organization such as a bank, the transactions reliance on mining means that they are not 100% secure.
Learn About the Threats to Stay Alert
As you peruse through the detailed how-to pieces below, make sure to pick the tactics that need technical abilities. Then, learn about such technicalities either directly on various forums or engaging a security specialist. Remember that you do not need to be a tech guru to protect your coins. Being knowledgeable helps to lower the risk of getting attacked, but there are no guarantees when it comes to cryptocurrencies.
The Cryptocurrency Risk You Face Largely Depends on You
According to Isaiah Sanju, a Cryptocurrency security expert, the risk that people will probably face depends on the total coins they hold and their daily transactions. Therefore, his advice for addressing such risks includes;
- As a new investor, make sure to keep careful track of the private keys.
- For casual investor, he advises that they watch for opportunistic threats. This can be achieved by hardening the email and online wallet security.
- For experienced investors, the best method is maintaining control over the private keys by staying away from web-based wallets and using hardware wallets. An air gap should also be used for enhanced security.
7 ways weak security/ accidents can risk investment in crypto coins
1: Losing or forgetting the private keys
The public ledgers used in cryptocurrencies do not have centralized documentation systems. This implies that if the wallet or private keys are lost, your coins would also be lost.
Yes, You Lose the Keys, You Lose the Coins
When people wake up and find they have lost the private keys to their wallets, they are left wondering how exactly everything unfolded. But this can happen easily in the following ways.
- Locking self outside the online wallet and losing access to the email that can be used to regenerate the password to get back the wallet.
- Losing the paper copy where you wrote the private keys the first time it was generated by the wallet.
- Losing the multi-factor authentication info when setting up a hosted wallet on a cryptocurrency trading platform.
- Keeping the backup keys in the same place with the main keys used on a daily basis and then, losing both copies.
The methods you can use to prevent losing the keys include
This can be summed up as being paranoid. This means the following:
-
- Carefully store the private keys and backup on different locations: This implies being extra cautious to ensure that you can easily recover the password in the case of a loss.
- Avoiding printing the private keys: Instead of printing the private keys, consider handwriting them. Many printers are designed with memories that can easily be hacked and the keys stolen by attackers. Even after making a handwritten copy, ensure to store it in a secure personal safe or a bank safe.
- Utilize true air-gapped cold storage options: This means operating without connecting to the internet. True air-gapped storage allows users to generate public keys and sign transactions offline. Then, transfer the keys and signed transaction using a USB device to your blockchain.
When it comes to cryptocurrencies, prevention is the only cure. Do not think of recovery because it will be too late.
2: Cryptocurrency Theft by Ransomware
In December 2017, NeceHash reported that it lost about $64 million in BTC during an attack on its system. NiceHash, a Slovenia based exchange, helps people to mine cryptocurrencies by leveraging unused CPU cycles on their computers.
Stealing computer data through ransomware has made many enterprises start installing ransomware defense systems as a priority. Cryptocurrency investors should also take note of the ransomware threat and take caution. Though the popularity of ransomware has gone down significantly in most industries, the crypto ransomware remains a serious threat especially to small businesses and individual investors.
What exactly is a ransomware attack?
 Ransomware attack happens when a code is injected into a computer, encrypts your data, and holds it hostage until a ransom is paid. Since cryptocurrencies are unregulated, it is possible for hackers to remain completely anonymous and demands payment in cryptocurrencies that are completely anonymous such as Monero.
Ransomware attack happens when a code is injected into a computer, encrypts your data, and holds it hostage until a ransom is paid. Since cryptocurrencies are unregulated, it is possible for hackers to remain completely anonymous and demands payment in cryptocurrencies that are completely anonymous such as Monero.
What is the rate of ransomware occurrence? The answer is, often. As more cryptocurrencies hit the market, and the value increases, the ransomware-as-a-service resources have become more common. This implies that more crooks are likely to make money without even investing funds into a malicious attack.
The Secret to Reducing the Threat from Ransomware
In many cases, the attacker notifies when it is very late with a frightening message that no business wants to get.
However, it is possible to recognize the exploits that make ransomware attacks possible. Get screenshots of the digital exchange accounts as well as the offline wallet files. It is crucial to learn to distinguish these two and the messages sent by Phishing attackers.
It is important to follow the rule of the thumb when trying to stay free from attacks; never follow links from emails unless you were expecting some specific communiqué. Instead, you should go directly to their website and initiate the conversation/ send a message.
Turn around the Odds of Ransomware in Your Favor
There are a number of highly effective methods that people can use to stay free from ransomware attacks. Here are some of them:
- Set the computer to search for and install updates automatically. The first step to staying free from ransomware is ensuring that your system is up-to-date. Many OS updates come with the latest security capabilities that help to keep respective devices extra secure.
- Install the right anti-virus/ anti-malware software. This sounds obvious? Yes. However, even ransomware still leaves digital signatures that can be picked by anti-malware software. Then, these strains can be used to discover threats and blocking them to avoid attacks.
- Keep your anti-virus solution up-to-date. Ransomware developers have perfected the art of identifying gaps and vulnerabilities when looking for methods of entry. Therefore, keeping your anti-malware up-to-date ensures all emerging gaps are fixed and vulnerabilities addressed. Remember to pick the anti-virus solution that can easily identify known and unknown threats.
- Always stay away from suspicious links and attachments sent to your email. Many ransomware attacks commence with a phishing strategy. When you click a malicious email and get redirected to a compromised site, your system is in the process of getting attacked. The best strategy is avoiding opening malicious links and attachments, especially from strangers.
- Disable the macros that are used by Microsoft docs. Many digital attackers always look for a place to hide their executable ransomware files. A macro is a great place for hiding such executable files. You need to stay away from suspicious attachments and macros completely.
- Install a good pop up blocker. Because most bad actors use maladvertising and email for delivery, an ad blocker will help to prevent opening of automatic ads on the websites you visit.
- Always backup data on the hard drive and cloud. This is very important because in the event of an attack, there will always be a fall back plan. These two methods of storing data are relatively cheap.
- Adopt and use air gaps. Consider strengthening your cryptocurrency security by adding air gaps to your current strategy.
Recovering From a Ransomware Attack
If you get attacked by ransomware, it is strongly advisable to use anti-malware tools to clear the threats before restoring data. Note that ransomware tools have become readily available in the market with some being provided free. However, you need to appreciate that this strategy will only work if you had installed a backup before the attack took place.
3: Stealing of Computer Resources via Cryptojacking
Early in 2018, a cryptomining botnet referred to as Smominru was discovered. This bot had infected over 500,000 computers in Russia, Taiwan, and India. It was targeted at Windows servers used to mine Monero. Proofpoint, a Cybersecurity firm, estimated that by close of January 2018, the bot had generated approximately $3.6 million.
The cryptocurrency attackers are also employing ransomware-like methods and compromised websites to make your computer mine coins for them.
Cryptojacking
Cryptojacking mainly works as a malicious infection that steals the target CPU resources to mine crypto coins for criminals.
These criminals employ phishing strategies to load the crypto mining codes on the target computer. They could also inject scripts through ads delivered via different websites. In many cases, hackers opt for both methods to optimize returns.
Note that in some cases, you could get ransomware and cryptojacking categorized together. However, this post uses the narrower definition of cryptojacking to refer only to cryptomining. .
How to Detect Cryptojacking
Unlike other attacks such as ransomware that often provide the victim with notices from hackers, you might not get any sign of cryptojacking. This is the reason you should do the following:
- Learn about cryptojacking threats. Note that your existing endpoint tools such as antivirus will not detect the threats.
- Be on the lookout for signs of overheating. The overheating comes from excessive use of the CPU. You could even have fan or processor failure.
- Carefully monitor your system for unexplained CPU activity. Be on the lookout for large spikes of your CPU when on and off the network.
- Go for a network monitoring solution. Cryptojacking can be easily detected using network perimeter solutions that analyze the traffic on your CPU. Consider such solutions as part of the cryptocurrency investment.
Avoiding Cryptojacking
Note that unlike other attacks that target siphoning away your coins, cryptojacking does not have a direct impact on the cryptocurrency investment. What it does is draining the computer resources that can result to system crashes and poor performance.
Because an optimally performing IT infrastructure is crucial to managing digital currencies, cryptojacking can be very expensive.
The following are some active measures you can use to avoid cryptojacking or identify it promptly.
- Install good ad-blocking extensions on your browser to help detect and block malicious scripts and block them.
- Keep all your web filtering tools updated to identify and block sites trying to deliver cryptojacking scripts.
- Maintain browser extensions by updating them regularly.
Halt the Flow of Computer Resources
When you establish that your computer resources were cryptojacked, you should stop their flow. Consider using the following steps immediately.
- Killing and blocking site-delivered scripts. If an in-browser JS attack hit your system, destroy the tab running the script. Start by noting the site’s URL and then block it. You should also install an anti-cryptomining tool to protect the system from further attacks.
- Update your system purge extensions. If an extension infected your browser, it is important to update all the extensions and clear the infected ones.
If you find it difficult to implement these strategies, do not hesitate to use an IT expert for assistance.
4: Phishing in Cryptocurrency
Phishing is a common exploit that targets infecting mobile wallet applications and other areas where the digital coins are stored. Here, it is important to appreciate that Phishing is a means to an end that is targeted at making the target expose the sensitive info such as the private keys.
The commonest method of sending phishing scams are worms and Trojan malware. They are carefully designed to trick users into opening attachments that contain malicious codes or clicking links pointing to fake sites.
Once you open such sites or attachments, the attackers will steal your info using the malware.
What Exactly Do Phishers Look For?
Phishers are mainly interested in getting private keys and other logins that can provide them with access to investors’ wallet. These cases surge when the price of Bitcoin prices goes up.
- Approximately 9% of people who use Kaspersky antivirus globally were victims of phishing attacks.
- In 2017, the Kaspersky Labs Anti-Phishing system was triggered close to 60 million times on Kaspersky users.
- Researchers at Kaspersky Labs detected 13 million more phishing attacks on clients’ computers in the 3rd quarter of 2017 compared to the previous quarter.
These attacks were mainly directed at financial organizations such as online stores, banks, and payment services.
Maintain a Watchful Eye for Phishing Attacks
The best tool to beat phishing attacks is a watchful eye and common sense. Therefore, before hitting open that email or attachment, here is what to do.
- Learn how to identify suspicious and phishing emails. You can take screenshots of emails from top businesses such as exchanges that handle crypto related info. Then, use them to note the differences.
- Be sharp in checking the source of info of all incoming mail messages. For example, what information is the sender looking for? Would a legitimate bank seek such info?
- Confirm that the sender is who he indicates to be. You can contact the sender on a different thread for confirmation.
- Confirm that you are the only recipient. In many phishing messages, the TO field that is supposed to have your name is often blank or with someone else’s name.
- Be on the lookout for emotional content. Phishing messages largely come with threatening language or very urgent requests that prompt immediate response.
- The message has an attachment that requires being opened for immediate action.
5: Breaking and Gaining Access into Your Crypto Wallet
On January 28th, 2018, a hacker gained access to Coincheck exchange and made away with close to $524 million in crypto coins. This attack has made the need for regulations to go a notch higher.
The break-in brought to fore two key issues of the current crypto market; the digital wallets are not amply secure, and the exchanges across the globe are wildly when it comes to info security expertise.
How Do Criminals Break Into Cryptocurrency Wallets
Cryptocurrency investors store their tokens in encrypted storages referred to as cryptocurrency/ digital wallets. They include.
- Hot wallets that store the tokens online and that are accessed using web browsers and applications.
- Cold wallets that store tokens offline.
Cybercriminals target deceiving the coin owners into downloading and installing malware designed to look like wallets. Once the target opens the files, a fake registration form is used to request the user’s personal details.
Before the investor knows what has happened, the malware moves his coins to another location. Here are the main methods that the criminals use to break into wallets.
- Crypto-stealing malware. This is one of the new malware in the industry. It is designed with the aim of stealing crypto coins by accessing the logins credentials or even the entire wallet.
- Initial Coin Offering (ICO) fraud. Because of the large number of coins in the market, many criminals are creating fake ICOs and running away once investors buy their ventures.
In December 2017, SEC closed down PlexCoin ICO which was thought to be a $15 million fraud.
Note that hackers can also spoof legitimate ICOs and trick investors into paying them as opposed to sending funds to the real company.
- Phone-porting. This happens when crybercriminals target stealing cell phone identity. Once the crooks get your number, they trick the provider to grant them control of the account. Then, they reset the password and route the coins to their wallets.
- Fake digital wallets. While it is a must to have a digital wallet, the biggest problem is identifying the fake ones from the genuine ones.
How to Avoid Digital Wallet Breaking
Avoiding digital wallet attacks requires the user to get obsessive with digital security. What does this mean?
-
- Performing due diligence. Prior to buying those tokens in an ICO, carefully review them and avoid rushing to the too good deals. You should be very cautious especially when offers come via email and social media channels.
- Strengthen the digital wallet security. Make sure to go for unique pins and even verification questions that hackers cannot easily know. You should even consider switching the 2-factor authentication from phone to Google Authenticator. The best method is keeping the coins offline.
- Harden your computer security. Install a reliable anti-virus program and firewall to protect the computer. Then, install a 2-factor authentication, a password manager, and deploy a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt the online connection.
- Consider using a dedicated computer. When you limit a device to only one function, moving the coins and keeping your investment safe becomes very simple.
6: Theft through Social Engineering
In mid-2017, one of the most popular Ethereum Classic exchanges was reported to be stealing funds users. Hackers employed social engineering to convince managers they were the actual owners before they started intercepting the cash flows.
Luckily, the exchange managers noted something was wrong and halted the process immediately. Lucking, the holders got their funds back.
Many Paths but One Goal: The Digital Deception
Note that the happy endings like the one just described above are rare. Social engineering is designed as a means to an end. Like Phishing attacks, there are a number of ways that crooks accomplish their mission.
The main method used in social engineering involves the crooks trying to convince scammers they are the legitimate owners of the wallets. Then, they divert the coins to their wallets.
Why Trust is Very Important in Cryptocoins
Most social-engineering based exploits involve presenting investors with false identities. This implies that it is prudent to know who the parties and entities you are dealing with when buying, storing, and selling coins. To detect related scams, here are some of the tips to look for.
- Being promised easy money.
- A great sense of urgency.
- Being asked to become a partner in unclear deals.
In order to avoid social engineering related scams, it is important to understand who to trust. This implies:
- Taking the habit of confirming companies, individuals and resources sending you emails. For example, if you want to purchase a mining rig, only buy from a trusted source.
- To invest in any cryptomining operation, ensure to verify the mining address.
- To remain on the correct path, only use known and good links. Do not simply click all the links sent to you.
- Always use common sense to question every move.
7: The Danger of Sending Funds to Wrong Address
Take to the crypto forums, and you will hear many people indicating they sent coins to the wrong addresses. Because the private and public keys are strings of numbers and letters, getting one of the characters wrong is all that is required to send the coins to the wrong person.
Avoiding Typos
Because of the built-in checking procedure when sending coins, typing the wrong characters would prevent the application from sending the cryptocurrencies into cyberspace. Well, this can be prevented but the user need to be prepared well before something wrong takes place.
Typos can be avoided by using good password management software. You should also use the copy and paste functions with a lot of care. Remember that the destination should be checked severally before hitting the send button.
Note that this loss mainly happens when sending the tokens to a wallet that holds related coins (think of a wallet that holds Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin). Though this problem can be solved theoretically, you would probably be out of luck in reality.
Avoiding Theft or Fraud
Unfortunately, many people lose track of their coins by sharing their private keys with criminals without realizing. Misplaced trust results in sending coins into an unchangeable one-way route to another person’s wallet. Note that many people claim they lost their tokens via typo because it is easier to explain it compared to others such as poor human judgment.
Source: https://www.bitira.com/cryptocurrency-security/
Which Cryptocurrency do you want to buy, transfer or store?
Trading and investing in digital assets is highly speculative and comes with many risks. The analysis/stats on CoinCheckup.com and it’s subsites are for informational purposes and should not be considered investment advice and or the truth. Statements and financial information on CoinCheckup.com and it’s subsites should not be construed as an endorsement or recommendation to buy, sell or hold.
Please do your own research on all of your investments carefully. Scores are based on averages of third party websites. Past performance is no indicative of future results. Read the full disclaimer here.